Judy Sims’ “Top 10 Lies Newspaper Execs are Telling Themselves” may be painful for newspaper execs to read, but they should read it anyway. In blunt language, she shoots down some of the most common rationalizations newspaper executives use for continuing to do business as usual. Not all of her points are thoroughly supported, but it’s hard to argue with the common-sense thinking behind most of them.
Among our favorite quotes:
The only way newspapers can ensure the survival of their brands and the journalistic principles they hold so dearly is to separate the Web organization completely from the newspaper.
This frames the list’s biggest “myth,” which is that news organizations can prosper online while doing what they’ve always done in print. The nature of online publishing is conversation and community, not top-down communication. Organizations that derive 90% of their revenue from print are never, ever going to give an online division the attention or resources it needs.
Figure out what is truly scarce information to your readers. Then, maybe you can charge for it.
Yes, yes, yes. Putting pay walls in front of information that doesn’t meaningfully affect people’s lives is a DOA idea, yet it seems to be conventional wisdom right now that readers will pay for stuff like popular columnists and exclusive sports coverage. No they won’t. They will pay for information that saves them money, enhances their appearance or finds them love, and precious little else. Maslow’s Hierarchy wasn’t invalidated by Internet.
We used the paper to help us shop every week…and decide what movie to see at what time and where. How much of the value of the newspaper was derived from news and how much was derived from all these other things? After all, news has always been free on TV and radio.
See the previous point. Publishers who think readers are going to pay for news are delusional. Not to mention pompous. Half the reason people subscribe to newspapers is for the coupons. News is a commodity. You have to deliver value that affects people’s lives in a meaningful way.
Figure out what is truly scarce information to your readers. Then, maybe you can charge for it…Do what you do best and link to the rest.
The second part of the quote is from Jeff Jarvis, but the sentiment is appropriate to the “myth” theme. Newspapers have traditionally had to do everything for their readers because readers had no way to find information for themselves. Now that restriction has been lifted, which means publishers should stop spending money on stuff they suck at.
The more cuts are made, the more newspapers are guaranteeing their own demise.
That’s because the people they’re cutting are setting up shop as hyperlocal bloggers and competing against their former employers. Newspaper layoffs are thus giving rise to the next breed of competitors.
If there’s any unifying thesis to Sims’ 10 lies, it is that trying to manage a revolution is futile. Publishers will not iterate themselves to a secure future, nor will they ever bring back the profit margins of the past. The rules have changed forever and that means blowing up a lot of stuff. The process is incredibly painful but it’s necessary for any organization that hopes to make it to the other side of this vortex.
A couple of weeks ago, SeattlePI.com reported that its Web traffic has remained unexpectedly strong after pulling the plug on its print edition and firing 80% of its staff. The Post Intelligencer may have given the rest of the industry a model for completing the transition to the digital world.
Get Comfortable with “Good Enough”
After you’re done reading about 10 lies, head over to Journalism Iconoclast Pat Thornton, who speaks much truth about what he calls the “Down and Dirty Revolution.” Thornton’s main point: Stop thinking like an entity that was the be-all and end-all of information to its community and start thinking like a participant in the digital community. What does that mean? Paraphrasing:
- Make the most of what you’ve got and stop whining about the resources you lack.
- Be satisfied with good enough. You can improve it later. Perfection is the enemy of getting stuff done.
- Stop duplicating effort. “If parents are taking pictures at a high school football game…it makes much more sense to work out a deal with them than to spend staff resources on taking pictures at said game.” So true. Likewise, use Creative Commons photos and stuff people post on Flickr instead of sending your own photographer to shoot the same stuff.
There’s more, but those are the basic themes.
Miscellany
If all goes well, we may soon remove the Claremont (N.H.) Eagle Times from the R.I.P. list. A federal judge has given a Sample, Pa. newspaper chain conditional approval to buy the newspaper with the intent to relaunch it. The 7,800-circulation Eagle Times closed abruptly in July when its owner ran out of money. It took with it three small weeklies, which also will be relaunched if new owner Sample News Group has its way. Owner George Sample said his goal is to relaunch the daily before the end of the month with a staff of 25, which would be significantly smaller than the 66 full-timers and 29 part-timers the paper previously employed. Sample also said he plans to relaunch the weeklies at some point. Sample offered just $261,000 for the franchise, which was nearly $4 million in debt when it declared Chapter 7 this summer.
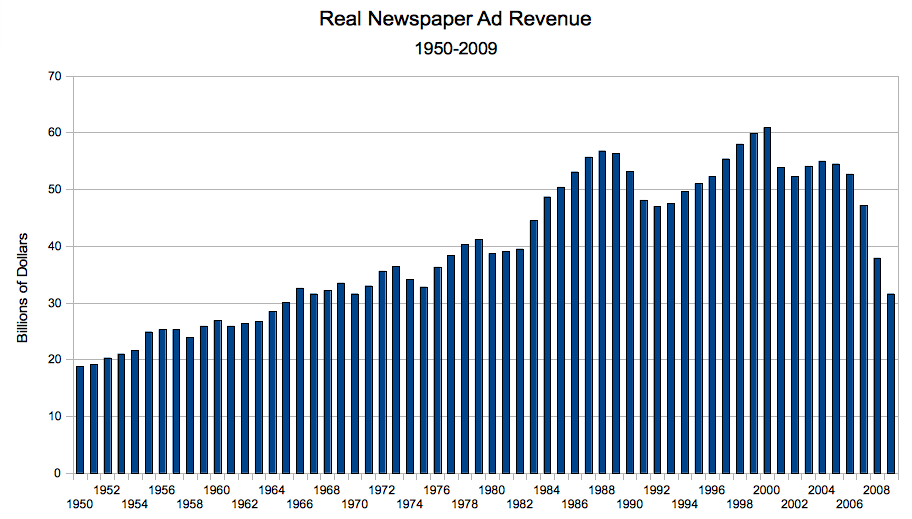
Ryan Chittum runs the numbers and finds that newspaper ad revenues are on track to hit their lowest level since 1965. In real dollars, revenues peaked in 2000. The comeback from the 2001-2002 recession was never very strong and sales have plummeted for the last three years. Real dollar revenue for 2009 will be about half of what it was just nine years ago, a stunning development in an industry that’s been historically known for its stability. Chittum also notes that circulation is the only slice of the revenue pie that’s growing right now while online advertising is declining. In fact, it appears that the online advertising business will only support one spectacularly successful business and that’s Google. A busy comment stream on this month-old piece debates whether online advertising is actually stealing share from print. Right, and global warming is a myth. (If you have trouble reading the chart below, click on it to go to Chittum’s analysis at the Columbia Journalism Review, where you can see an enlarged version.)
PaidContent.org has an interview with Josh Cohen, senior business product manager of Google News. Cohen has been schooled well to say little in a lot of words, so don’t expect any great insights. The main takeaway for us was that Google has no intention of sharing with publishers any revenue generated on Google’s site but that the company really wants to work with news organizations to make sure content behind pay walls is visible to Google’s search engine. In conversations like these, we hear Google executives sounding more and more like Microsoft officials did in the early 90s.
Speaking of Google, have you seen Google Fast Flip? It’s a new Google Labs project that “lets you browse sequentially through bundles of recent news, headlines and popular topics, as well as feeds from individual top publishers,” according to an entry on the Official Google Blog. “As the name suggests, flipping through content is very fast, so you can quickly look through a lot of pages until you find something interesting.” The service is the product of a partnership between Google and “three dozen top publishers, including the New York Times, the Atlantic, the Washington Post, Salon, Fast Company, ProPublica and Newsweek.” The idea is that if people can access news more quickly, they’ll read more news and that will result in more advertising revenue. Google continues to try to extend the olive branch to publishers who see nothing to like in other Google services that they claim steal their intellectual property.
Final bids for BusinessWeek are due today and Bloomberg LP is reported to be the leading contender. Other possible buyers include Bruce Wasserstein, Lazard, OpenGate Capital and ZelnickMedia, but Bloomberg is said to have the top bid. BusinessWeek revenues are on track to be down 43% from last year’s levels.
 The cure for the newspaper industry’s ills was once thought to be a “hyper-local” focus, but that’s not proving to be the salve for New York City, which is suffering an unprecedented decline in local news coverage. The latest casualty is the New York Daily News, which on Monday said it would cut its newsroom staff by half. The Washington Post points out that this means that a paper that employed 400 journalists in 1988 will have a reportorial staff of just 45 when the latest cuts new owner Tronc take effect.
The cure for the newspaper industry’s ills was once thought to be a “hyper-local” focus, but that’s not proving to be the salve for New York City, which is suffering an unprecedented decline in local news coverage. The latest casualty is the New York Daily News, which on Monday said it would cut its newsroom staff by half. The Washington Post points out that this means that a paper that employed 400 journalists in 1988 will have a reportorial staff of just 45 when the latest cuts new owner Tronc take effect. In it, Loyola journalism professor Michael Giusti (right) makes a misguided assumption that the
In it, Loyola journalism professor Michael Giusti (right) makes a misguided assumption that the 


 After nearly losing its two daily newspapers a year ago,
After nearly losing its two daily newspapers a year ago,  Go to the basic
Go to the basic 









