Mark Glaser invites two big thinkers on opposite sides of the micropayment debate – Techdirt’s Mike Masnick and The New York Times‘ David Carr – to spar with each other and try to reach some common ground. The result is what you’d expect when you put two talented writers into competition with each other: Great wordplay and eventual meeting in the middle.
Both combatants agree that putting paywalls in front of existing content is suicidal, although Carr believes that citizens will shell out once they realize that the alternative is cacophony. Masnick wins the award for best imagery: Paywalls are “putting up a tollbooth on a 50-lane highway where the other 49 lanes have no tollbooth,” he writes. He sees no merit in paywalls whatsoever, while Carr believes they can work in some scenarios.
Carr suggests that micropayments should be looked upon “as payments for news applications instead.” In fact, the Times’ media columnist never suggests that charging readers for what they now get for free is a viable strategy. But since the status quo is no longer viable, shouldn’t publishers experiment aggressively with hybrid models?
In the end, that’s where the debaters end up. Both agree that blended paid and ad-supported models have the greatest chance of success. And if you re-read the first part of the two part series, you see that both basically suggested that approach at the outset. So maybe the “debate” was a bit of a fabrication to begin with, but at least it got our attention. And isn’t that the goal after all?
Media Employment Trend Not All Bleak
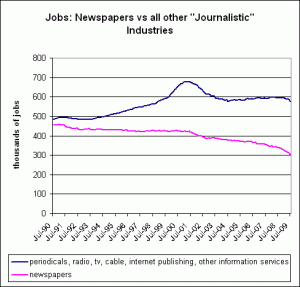
Over at BusinessWeek, Michael Mandel is looking at employment in US information industries. Using Bureau of Labor Statistics figures, he finds evidence that “someone is hiring out there,” but it isn’t newspapers, which have seen employment fall by about 40% since 1990. Mandel’s analysis goes beyond newspaper employment to look at job trends in broadcast, Internet and “other information services.” What’s interesting is the growth in the “other” category. It’s the only segment of the market that’s above Internet bubble employment levels (although the actual numbers are quite small). Mandel promises more analysis in future posts.
Jeff Jarvis takes issue with Mandel’s whole premise, calling it “measuring the wrong economy: the old, centralized, big economy. In both cases, he misses new value elsewhere in the small economy of entrepreneurs and the noneconomy of volunteers.” In Jarvis’s view, media isn’t dying so much as restructuring itself in a “post-industry” model characterized by vastly more efficient means of production, a distributed workforce and a decentralized approach to nearly everything. Innovation hasn’t left the building, he says, it has merely left the buildings where priesthoods dwell. To see the new media economy taking shape, you have to look at Wikipedia and eBay for guidance, not The New York Times and Macy’s.
Miscellany
It’s a two-horse race to own the Boston Globe, and one horse just got stronger. Former Globe executive Stephen Taylor has been joined by his cousin Benjamin in a bid for the Globe and its sister Worcester Telegram that’s estimated at $35 million plus the assumption of $59 million in pension obligations. Benjamin Taylor was the last member of the Taylor family to serve as publisher; he was ousted by owner New York Times Co. in 1999. The Taylors are squared off against Platinum Equity Partners, a Beverly Hills-based investment firm that successfully purchased the San Diego Union-Tribune earlier this year and that is bidding on several other newspapers around the country. A third potential bidder headed by private-equity executive Stephen Pagliuca has dropped out of the race, with Pagliuca instead electing to run for Sen. Edward Kennedy’s vacant Senate seat.
Members of the Boston Globe chapter of the Newspaper Guild have launched a petition drive to oust the chapter’s seven-member executive committee. Disgruntled union members seem to think they got a raw deal because negotiators at first rejected management’s call for pay cuts, only to later accept an even worse deal after the New York Times Co. drew a line in the sand.
We’ve been hearing anecdotally for some time that community newspapers are faring better than their big-city brethren. Now the organization called Suburban Newspapers of America has the numbers to back it up. Ad revenue at community papers was off 12.4% in the second quarter compared to a year ago. In contrast, major metros saw declines of 29%. Community papers are also seeing earlier slowing of the rate of decline, which indicates that the worst may be over, at least for now.
A federal judge has cleared the way for the Minneapolis Star Tribune to emerge from bankruptcy next week. The newspaper that McClatchy Corp. paid $1.2 billion for in 1998 is now essentially worthless, its fate being in the hands of a committee of secured creditors who will choose a new publisher to replace Chis Harte, who’s stepping down. New board members include former Wall Street Journal publisher L. Gordon Crovitz and GateHouse Media head Michael E. Reed.
Red-faced board members at The New York Times Co. have had to withdrawn compensation awarded to Chairman Arthur Sulzberger Jr. and CEO Janet Robinson because stock option grants and bonus compensation exceeded company policy. Sulzberger and Robinson will have to give back some stock options and agree to a $3 million cap on bonus compensation if they exceed all their goals, compared to the $3.5 million originally promised.
Robert Niles has an inspiring essay on Online Journalism Review about Eight things that journalism students should demand from their journalism schools. We particularly like #8: “Passion, not excuses.” If you’re associated with a J-school, ask if this description applies to your faculty: “Instructors [who] complain about the state of the news business, griping how much better it used to be and how awful bloggers/forums/websites are.” Pining for the old days isn’t going to help anyone build a career in the new journalism economy. Niles asks for teachers who are fired up about the new model of journalism and who can inspire passion in their students. He also suggests that students use the new tools of publishing to build a base of followers before the job-seek. “Who ya gonna hire?” he asks. “The student with potential… or the student who’s already got 50,000 unique readers a month?”


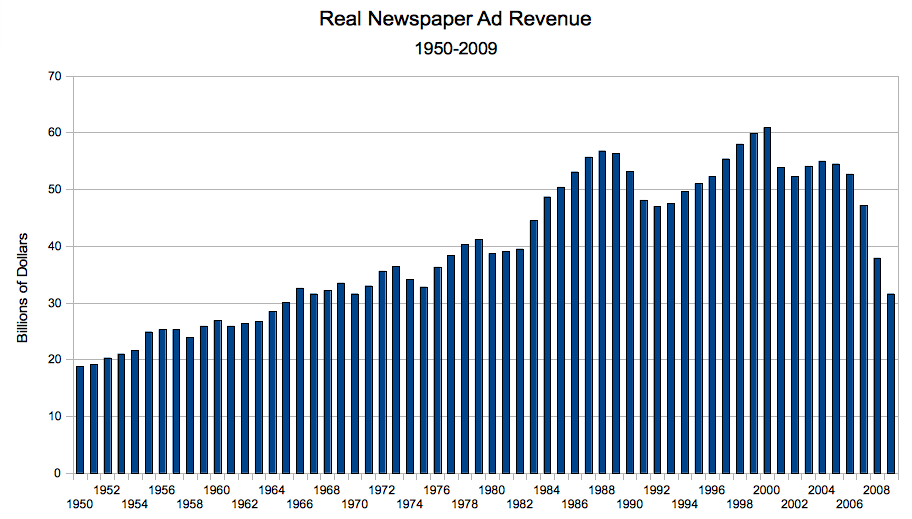
 Alan Mutter interviews Jeremy Halbreich
Alan Mutter interviews Jeremy Halbreich

 Newspaper layoffs have hit young people the hardest
Newspaper layoffs have hit young people the hardest