Perhaps all those fresh-faced young journalism wannabes who are flooding J-schools across the country right now know something we graybeards don’t. While there’s still plenty of legitimate hand-wringing going on over the collapse of publishing institutions, some media seers are beginning to see promise where others see peril.
 David Carr’s essay in The New York Times last weekend is drawing considerable attention and well-deserved praise for its glass-is-half-full perspective. Carr, who put in his time at the traditional media watering trough, observes that the technology-enabled young journalists he meets these days increasingly see the collapse of hidebound media institutions as an opportunity to make a name for themselves based upon merit rather than survival. “The next wave is not just knocking on doors, but seeking to knock them down,” he writes. “Young men and women are still coming [to New York] to remake the world, they just won’t be stopping by the human resources department of Condé Nast to begin their ascent.”
David Carr’s essay in The New York Times last weekend is drawing considerable attention and well-deserved praise for its glass-is-half-full perspective. Carr, who put in his time at the traditional media watering trough, observes that the technology-enabled young journalists he meets these days increasingly see the collapse of hidebound media institutions as an opportunity to make a name for themselves based upon merit rather than survival. “The next wave is not just knocking on doors, but seeking to knock them down,” he writes. “Young men and women are still coming [to New York] to remake the world, they just won’t be stopping by the human resources department of Condé Nast to begin their ascent.”
We found ourselves nodding vigorously as we read this piece. Carr expresses no nostalgia for an industry that was built on the inefficiencies of traditional advertising that are now being Googled out of existence. Career paths that relied upon young journalists doing “marginal jobs for indifferent bosses doing mundane tasks” are being vaporized and replaced by a meritocracy in which the best may not only survive but thrive. We’re still a long way from the Promised Land, and it’s a scary world if your job security is based upon having outlasted everyone else, but it’s invigorating if you’re young, energetic and enabled with all the trappings of today’s technology.
New York City venture capitalist Fred Wilson agrees. “I believe the move from a velvet rope model to a meritocracy is a good thing and that the new media business we are building in the wake of the old one will be a better media business; leaner, faster, and controlled more by users than media moguls,” he writes. Amen. As sympathetic as we are to the many people whose careers and lives have been thrown into chaos by the collapse of traditional media, we continue to see a much brighter future once the wreckage is cleared away.
AOL to Automate the News
 America Online, which recently announced plans to lay off a third of its employees, is breaking some new ground in the newsgathering field. The company plans to use automation to crawl the Web looking for stories that its visitors have indicated they prefer through their clicks and page views. The robot will then advise a team of increasingly dehumanized editors when and where to publish what it finds. AOL will also use its new venture, Seed.com, to outsource assignments to an army of (presumably low-paid) reporters and photographers.
America Online, which recently announced plans to lay off a third of its employees, is breaking some new ground in the newsgathering field. The company plans to use automation to crawl the Web looking for stories that its visitors have indicated they prefer through their clicks and page views. The robot will then advise a team of increasingly dehumanized editors when and where to publish what it finds. AOL will also use its new venture, Seed.com, to outsource assignments to an army of (presumably low-paid) reporters and photographers.
It sounds impersonal and even a little creepy. The idea of building a new site based entirely upon the preferences of viewers strikes us as a little like the model at Digg.com, which generates boatloads of traffic, but tends toward stories about video games and loopy kids. Digg isn’t threatening to upend CNN.
Writing on FastCompany.com, Kit Eaton makes an interesting case for AOL’s actions creating a revenge effect. If social media is actually adding more of a human element to interactions between groups, does a service that removes much of the human decision-making make any sense? Eaton proposes that readers today actually expect more of the human element in their news coverage rather than less. Of course, we haven’t seen the AOL technology in action and human editors could tweak the parameters over time to make its selections look more like The New York Times. But we doubt it.
Miscellany
Last week we told you about a new daily newspaper that is being launched into the Detroit market, hoping to fill a void left by the reduced publication schedules of the two major dailies there. Well, the experiment didn’t last long. The Detroit Daily Press published just five issues before hitting “a bump in the road” and suspending further operations until the new year. The suspension was blamed on “lack of advertising, lateness of our press runs and lack of distribution and sales,” according to an announcement on the publication’s Facebook page. This sounds to us like more than just a pothole, but we hope the owners, who have courted this market before, can overcome their troubles and come back in 2010. Photographer Rodney Curtis offers an insider’s perspective. Having lost his job at the Detroit Free Press earlier this year, he’s now a double-dip victim of the industry’s troubles.
Some local television stations are now crowdsourcing the news assignment process. Broadcasting & Cable reports on stations in Milwaukee, Lancaster, Pa. and Little Rock that are opening their daily news budget meetings to outsiders through video, live blogs and Twitter. News directors say the experiment has been a mixed bag, since audiences that sometimes number over 100 can get stuck on gossip and minutia instead of general interest stories. However, they say the open-air meetings have also resulted in solid news tips, such as the WITI (Milwaukee) story on a father surprising his son at school upon returning from Iraq. The boy’s teacher had clued the station about the visit.
Add MediaNews and A.H. Belo to the short list of newspaper publishers who are considering joining Rupert Murdoch in his crusade against Google’s evil empire. Executives at both companies were quoted recently saying that they may withhold some paid content from Google’s search spiders. However, they indicated that they would not block access to free content. These statements are a minor blow to Google, which says it can work perfectly well with paid content and that publishers using paywalls need Google even more to make their content discoverable.
The Hopi Tribal Council has decided to close down the Hopi Tutuveni, which is the primary newspaper covering Hopi lands. The 6,000-circulation paper, which has been publishing since the 1970s, was called “ineffective” by one tribal Council maker and didn’t merit continued funding by the budget-pressed group.
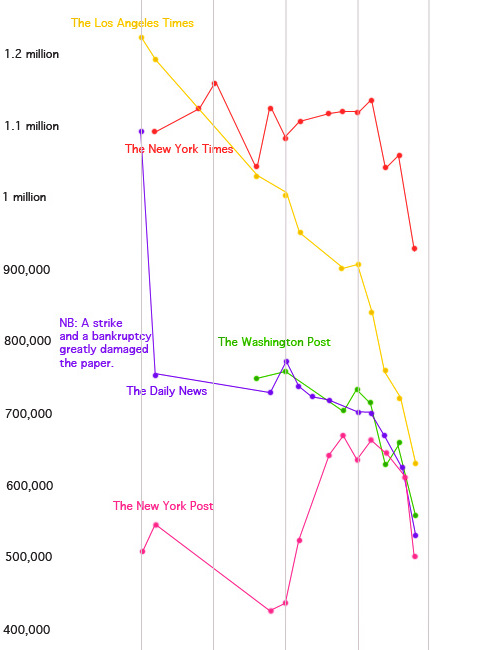
It’s the end of an era, of sorts, at the Washington Post. The paper plans to close down its last three domestic bureaus – in New York, Los Angeles and Chicago – at the end of this month in a significant retrenchment that focuses on the Washington area. The move continues a recent trend toward embattled big-city dailies shutting down the remote offices as they attempt to go hyperlocal. David Carr quotes Post Executive Editor Marcus Brauchli as saying “We are not a national news organization of record serving a general audience.” The Wall Street Journal announced plans to close its Boston bureau last month.
 After nearly losing its two daily newspapers a year ago,
After nearly losing its two daily newspapers a year ago,  Go to the basic
Go to the basic