Management at the Boston Globe finally wore down union leadership last night and won tentative agreement on a revised contract that is substantially similar to the one the union rejected a little over two weeks ago. The new contract slightly reduces the pay cut management had originally sought, although it includes additional benefit reductions. More importantly, the Globe and its parent New York Times Co. emerged victorious on the biggest issue: the right to end lifetime job guarantees for 170 employees.
Union members still have to ratify the proposed contract in a vote set for July 20, but approval seems likely now that union leadership has endorsed the deal. The end of the last bitter labor dispute between Globe management and employees also positions the paper for sale to one or more of several interested suitors, which include investor and Boston Celtics co-owner Stephen Pagliuca,; Partners HealthCare chairman Jack Connors and former Globe executive Stephen Taylor.
Schedule Cutbacks Have Unforeseen Effects
More than 100 daily newspapers in 32 states have cut at least one daily edition in an effort to reduce costs and avoid layoffs. But if you think that changing frequency is a matter of just shuttling around the work schedule, read this excellent piece in Editor & Publisher on the ripple effects of becoming somewhat-less-than-daily. Joe Strupp talked to editors around the country and found that cutting as little as one day’s worth of print news can force significant changes in the way a newspaper approaches its mission. “We try to cover Saturday through Monday on Tuesday. But we don’t staff Sunday night so we can staff more the rest of the week. There is more breaking news that goes up on Monday,” says Dan Liggett of the Wilmington (Ohio) News Journal in a quote that typifies the kind of calendar soup that these editors must contend with.
Some papers have had to add pages on days following gaps in the production schedule because print diehards still want local news and won’t go online for it. Big news stories tend to lose momentum when they occur just before a break in the production schedule. This forces editors to alter subsequent coverage to keep reader interest from waning. The Detroit News and Detroit Free Press, which are the most prominent dailies to cut back on print, have moved more enterprise reporting stories into the Thursday, Friday and Sunday editions that land on subscribers’ doorsteps.
In communities with active high school sports schedules, the loss of a Saturday edition has prompted website editors to boost the priority of local sports in Saturday online coverage and to add Sunday pages to handle the demand. Other publishers have found that weekly columns and features that appeared on certain days have had to be moved to other days because readers didn’t want to give them up.
The good news is that “editors are becoming more convinced that print-devoted readers will stick around even when fewer editions are available and stories get published days after a news event,” Strupp concludes.
R.I.P. Ann Arbor News
 The Ann Arbor News, which announced plans in March to scale back from daily to twice weekly frequency, is apparently going a little further than that. Writing on Poynter.org, Rick Edmonds reports that the 174-year-old daily is effectively shutting down. The “unspecified number of layoffs” the paper announced in March is in fact the entire staff, Edmonds says. The headquarters building (right) will be sold and an entirely new online operation launched with a twice-weekly print edition that looks pretty lightweight. Staffers will have the opportunity to apply for jobs at a much lower pay scale than what most of them are currently earning. Edmonds suggests that Ann Arbor’s young, hip college-age crowd is more attuned to online media and extrapolates the same scenario playing out in cities like San Francisco, Boston, Minneapolis, Seattle and San Jose, where a young, upwardly mobile populace creates a hostile environment for a daily newspaper.
The Ann Arbor News, which announced plans in March to scale back from daily to twice weekly frequency, is apparently going a little further than that. Writing on Poynter.org, Rick Edmonds reports that the 174-year-old daily is effectively shutting down. The “unspecified number of layoffs” the paper announced in March is in fact the entire staff, Edmonds says. The headquarters building (right) will be sold and an entirely new online operation launched with a twice-weekly print edition that looks pretty lightweight. Staffers will have the opportunity to apply for jobs at a much lower pay scale than what most of them are currently earning. Edmonds suggests that Ann Arbor’s young, hip college-age crowd is more attuned to online media and extrapolates the same scenario playing out in cities like San Francisco, Boston, Minneapolis, Seattle and San Jose, where a young, upwardly mobile populace creates a hostile environment for a daily newspaper.
Miscellany
Editor & Publisher continues to try to find insight in the increasingly meaningless “time-spent-on-sight” statistics for major newspapers. We pointed out some of the weaknesses of this metric in our analysis of last month’s figures, including the paradoxical fact that big spikes in traffic can actually drive down time-spent figures. Did the Washington Post really do anything to deserve a one-third drop in reader time commitment from May 2008 (16:04) to May 2009 (10:58)? If you look at the snapshot for those two months, things look pretty negative for the Post, but the April 2008 time-spent number was 12:55, which hints that the figure from May of last year was a fluke. We wish Nielsen would stop flouting these monthly snapshots and concentrate instead on six month moving averages, which would filter out the short-term spikes that make year-to-year comparisons practically useless.
Fans of Jim Hopkins’ hugely popular Gannett Blog can breathe a sigh of relief. The crusade to be the world’s most reliable source about what’s going on inside the company will continue at Gannettoid after the blog shuts down on July 19. Gannettoid is “a Web site that serves as a collection of stories, links and other Web sites about Gannett Company.” While it isn’t formally affiliated with Gannett Blog, Gannettoid is welcoming devotees to continue their conversations in the forum section. No word on whether Hopkins will pop in for a visit now and then.
The new owners of the San Diego Union-Tribune are already selling off property acquired in the purchase of the newspaper last month. Two properties have gone on the market at a combined sale price of $9.1 million, which is nearly 40% higher than what Platinum Equity paid for them. The move would tend to confirm Ken Doctor’s theory that Platinum Equity acquired the U-T primarily for its real estate value and got the newspaper thrown in for free. (via Gary Scott)
Sun Newspapers will eliminate 115 full- and part-time positions in mid-August as part of a sweeping reorganization plan that will reduce the company’s portfolio of weekly newspapers by half and outsource accounting, payroll and home delivery to the Cleveland Plain Dealer. Both organizations are owned by New Jersey-based Advance Publications.
The Columbia Journalism Review profiles Alan Mutter, whose Reflections of a Newsosaur blog has stirred up the industry and created a launch pad for Mutter’s ideas about reinventing news organizations. It’s a good companion to our Feb. 18 audio interview with Mutter that includes details about his new ViewPass venture, which seeks to give publishers a viable subscription model.
 Washington Post publisher Katharine Weymouth addressed graduates of the Medill School Of Journalism at Northwestern University over the weekend, urging them to continue to fight the good fight and declaring that “the need for great journalism is stronger than ever.” You can read the full text of her address here. Dan Gillmor tweeted that it was a “defensive commencement speech by WashPost publisher; she plainly has no strategy for future.” However, Weymouth’s remarks indicate that she understands that the old model is collapsing and that publishers must adapt to a new world in which they are no longer “a toll booth over a bridge” to their readers. Read the text and draw your own conclusions.
Washington Post publisher Katharine Weymouth addressed graduates of the Medill School Of Journalism at Northwestern University over the weekend, urging them to continue to fight the good fight and declaring that “the need for great journalism is stronger than ever.” You can read the full text of her address here. Dan Gillmor tweeted that it was a “defensive commencement speech by WashPost publisher; she plainly has no strategy for future.” However, Weymouth’s remarks indicate that she understands that the old model is collapsing and that publishers must adapt to a new world in which they are no longer “a toll booth over a bridge” to their readers. Read the text and draw your own conclusions.
Last week we noted that MySpace is struggling against Facebook and other adult-oriented social networks, calling into question the effectiveness of Rupert Murdoch’s management strategy. Now MySpace is laying off two-thirds of its international workforce, or 300 people, on top of the 400 laid off in the US last week. Altogether, the company has cut its total workforce by nearly 40%. Which only goes to show, we suppose, that media dislocation isn’t limited strictly to old media.
And Finally…
 There is hope for veteran journalists. Oyster Hotel Reviews is a fledgling online venture that employs 13 journalists to conduct extensive reviews of lodgings for business and leisure travelers. The site, which is funded by Bain Capital Ventures, bucks the current trend toward wisdom-of-crowds reviews by employing professionals to visit hotels under cover and write about their experiences. “Oyster.com is a great opportunity for these journalists as they provide full benefits, competitive salary and a job that includes travel to various hotels around the world fully paid for—who wouldn’t want that as a job?” a publicist wrote us. We’re wondering where to apply.
There is hope for veteran journalists. Oyster Hotel Reviews is a fledgling online venture that employs 13 journalists to conduct extensive reviews of lodgings for business and leisure travelers. The site, which is funded by Bain Capital Ventures, bucks the current trend toward wisdom-of-crowds reviews by employing professionals to visit hotels under cover and write about their experiences. “Oyster.com is a great opportunity for these journalists as they provide full benefits, competitive salary and a job that includes travel to various hotels around the world fully paid for—who wouldn’t want that as a job?” a publicist wrote us. We’re wondering where to apply.

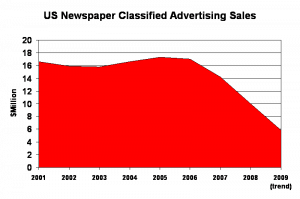

 There’s plenty of buzz in the blogosphere about an
There’s plenty of buzz in the blogosphere about an 

 , the Los Angeles Times and the Toronto Globe and Mail.
, the Los Angeles Times and the Toronto Globe and Mail. Newspaper cutbacks
Newspaper cutbacks 


