We’ve been working our way through the social media and journalism sections at OurBlook, a Web venture that seeks to combine some of the best attributes of blogging and in-depth book writing. Editor Gerry Storch and Founder Paul Mongerson, who both have extensive media experience, have posted more than 50 interviews and first-person opinion pieces from people who care about the future of journalism. We haven’t read them all yet, but here are some excerpts we noted from the 35 or so we’ve completed so far. More will follow later.
OurBlook is inviting more people to contribute to the discussion by signing up on its website. What’s a blook? It’s a cross between a blog and a book.
From Robert Brown on Social Media
Brown is President of RDB Consulting
“Web analytics is the mechanism that will drive the proliferation of targeted messaging across the Web to users via the ever-growing array of social media tools…[Mike] Orren [founder of Dallas-based Pegasus News] calls this convergence of media into one vast network ‘Web 3.0.’ The idea of a single website as a source of content is quickly becoming archaic. As Orren says, …’With Web 3.0, it no longer matters where the information lives. Once you post something, it will be quickly disseminated via social networks to those users who care about the information.’”
From Joe Shea on the Future of Journalism
Shea is editor-in-chief of The American Reporter
“The biggest issue is the failed model. Journalists need to own their own news publications, not simply toil for the people who own them…[T]here’s really no point in supporting other people with our work when we can support ourselves with it. The American Reporter was founded to make that possible when journalists are ready for it. We don’t care how long it takes; we always knew they would be slow to get off the corporate teat and start walking on their own. When that happens, and great news organizations owned and operated solely by journalists who are their own bosses exist all around the world – that’s when a newspaper war will erupt, and the world will find journalism anew. It won’t be so boring then.”
From Michael Saffran on the Future of Newspapers
Saffran is addjunct professor of communication at Rochester Institute of Technology
 “Lifting the newspaper/broadcast cross-ownership ban could benefit both newspaper and radio industries; however, rather than serving as an open-ended gift to media conglomerates, repealing the ban should be tied to stricter radio ownership limits. According to an FCC study, newspaper/television station cross-ownership enhances the quantity and quality of TV news and public-affairs programming. Radio could similarly benefit from partnerships between broadcasters and publishers because most newspapers (with a few notable exceptions) are, much like radio, inherently local. Thus, the addition of print reporters to the small news staffs (if they exist at all) of cross-owned radio stations could enhance local-radio news … an area in which local radio is currently underperforming.”
“Lifting the newspaper/broadcast cross-ownership ban could benefit both newspaper and radio industries; however, rather than serving as an open-ended gift to media conglomerates, repealing the ban should be tied to stricter radio ownership limits. According to an FCC study, newspaper/television station cross-ownership enhances the quantity and quality of TV news and public-affairs programming. Radio could similarly benefit from partnerships between broadcasters and publishers because most newspapers (with a few notable exceptions) are, much like radio, inherently local. Thus, the addition of print reporters to the small news staffs (if they exist at all) of cross-owned radio stations could enhance local-radio news … an area in which local radio is currently underperforming.”
From If Newspapers Fold, We’ll Adjust by Gerry Storch
Storch is the editor of OurBlook
“I think what will replace the newspaper in [my hometown of] Naples, [Fla.], and newspapers elsewhere, will be a pricy on-line newsletter. It will have a cheap, barebones staff to cover the basic business of the town – the city council, the school board, the police beat – and a couple veteran pros to provide an insider’s knowledge of what’s going on and make it worthwhile for readers to cough up $100 a month for a subscription, or whatever it costs to make a profit. So people who want straight news will still be able to get it. The media will continue but in a much different form, and they won’t be the mass media any more.”
From Paul Conti on the Future of Newspapers
Conti is an instructor in communications at the College of Saint Rose in Albany, N.Y.
 “Frankly, my students want and expect everything ‘on demand.’ They are not specifically loyal to media brands. They do not care what the source of their media content is as long as it entertains or informs them. If I were running a newspaper’s city room, I’d be sprinting to create more ‘TV News Stories’ that people can watch on their websites. A few newspaper companies are doing this, but the vast majority [of them] simply send one of their print reporters out into the field with a substandard consumer camera to record a news conference. Yes, that’s content, but it isn’t good content and it won’t attract younger readers. They need to mimic the styles that TV reporters do with visualizing stories. Every story in the newspaper should have a companion video version available on demand.”
“Frankly, my students want and expect everything ‘on demand.’ They are not specifically loyal to media brands. They do not care what the source of their media content is as long as it entertains or informs them. If I were running a newspaper’s city room, I’d be sprinting to create more ‘TV News Stories’ that people can watch on their websites. A few newspaper companies are doing this, but the vast majority [of them] simply send one of their print reporters out into the field with a substandard consumer camera to record a news conference. Yes, that’s content, but it isn’t good content and it won’t attract younger readers. They need to mimic the styles that TV reporters do with visualizing stories. Every story in the newspaper should have a companion video version available on demand.”
From Sean Dougherty on the Future of Journalism
Dougherty is vice president at Stern + Associates, a public relations firm
“I am one of those old timers and I love print newspapers, ink stains and all, but that is no reason to ignore reality: the value of the placement is the journalist’s brand and reach, not whether or not the information originally appeared on paper. Online articles get forwarded, increasing influence. Bloggers prefer to blog about topics where they can link through to what they are commenting on. Online articles are more easily fed into your own distribution channels, whether it is a personal blog, e-mail distribution list or website. While streamed video clips are usually associated with sketch comedy like ‘Saturday Night Live’ or ‘The Daily Show,’ it is unlikely that Harvard University Professor Michael Porter’s recent interview on ‘The Charlie Rose Show’ was seen live as often as it was viewed online based on the number of bloggers who linked to the segment.”
From Andrew Degenholtz on the Future of Journalism
Degenholtz is president of ValueMags, a magazine subscription marketing agency
“Many anticipate that the modern day journalist will morph into the ‘backpack journalist,’ where not only good writing and grammar skills will be valuable, but taking photographs and shooting video will almost become a necessity. As we’ve already seen, the ‘citizen journalist’ also plays a large role in this new media landscape. Bloggers getting press passes to news events once reserved for the traditional media will only help hungry consumers get even more specialized information. But one thing remains the same: good writing is still good writing. That won’t ever change. If you have something to say, people will read, no matter how it’s packaged.”
From Nigel Eccles on Future of Papers
 Eccles is co-founder and CEO of UK website hubdub.com, “a prediction market where people trade predictions on the outcome of running news stories or future events.”
Eccles is co-founder and CEO of UK website hubdub.com, “a prediction market where people trade predictions on the outcome of running news stories or future events.”
“Blogging is not nearly as big in the UK as it is in the US. For example, there are only a handful of high quality political blogs [in the UK] compared with hundreds in the US. One of the reasons that blogging is so popular in the US is that it is written in an informal and familiar style and tends towards sensationalism. The UK press is much closer to that style than the US press (where every other article seems like it is written for the Pulitzer Prize committee).” (Telegraph.co.uk photo)
From Paul Swider on Papers’ Future
Swider was a reporter with the St. Petersburg Times until he was laid off in May, 2008
“The larger issue, and the one that makes me so ‘popular’ with my erstwhile journalism colleagues, is humility, or its lack in the newsroom. Most reporters are well-meaning and believe they are doing a public service, but that is a legacy from an era when there wasn’t that much information available to the general public. Now that there is, to persist in the attitude that the newspaper is the source of all information is kind of silly. Most government meetings are televised, many documents are publicly available, dissatisfied workers that were the source for many an exposé can now publish directly themselves to the Web, so a journalist isn’t as indispensable as before, and may be superfluous in some contexts.”
From Louis Sarmiento on Social Media
The interviewer comments, “Big-name athletes and entertainment celebrities seem to have taken to Twitter because 1) they can control their message, 2) the message is short and non-taxing, 3) they bypass reporters, 4) they can have ‘contact’ with fans that really isn’t contact and 5) fans end up thinking they have contact though they really don’t.”


 The Ann Arbor News, which
The Ann Arbor News, which 

 David Healey lost his job at a small Maryland daily recently thanks to downsizing. He didn’t like being cut off from his community, so he started
David Healey lost his job at a small Maryland daily recently thanks to downsizing. He didn’t like being cut off from his community, so he started 


 , the Los Angeles Times and the Toronto Globe and Mail.
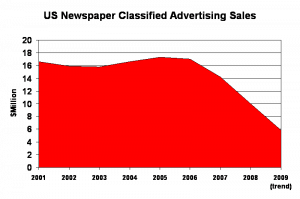
, the Los Angeles Times and the Toronto Globe and Mail. Newspaper cutbacks
Newspaper cutbacks 


