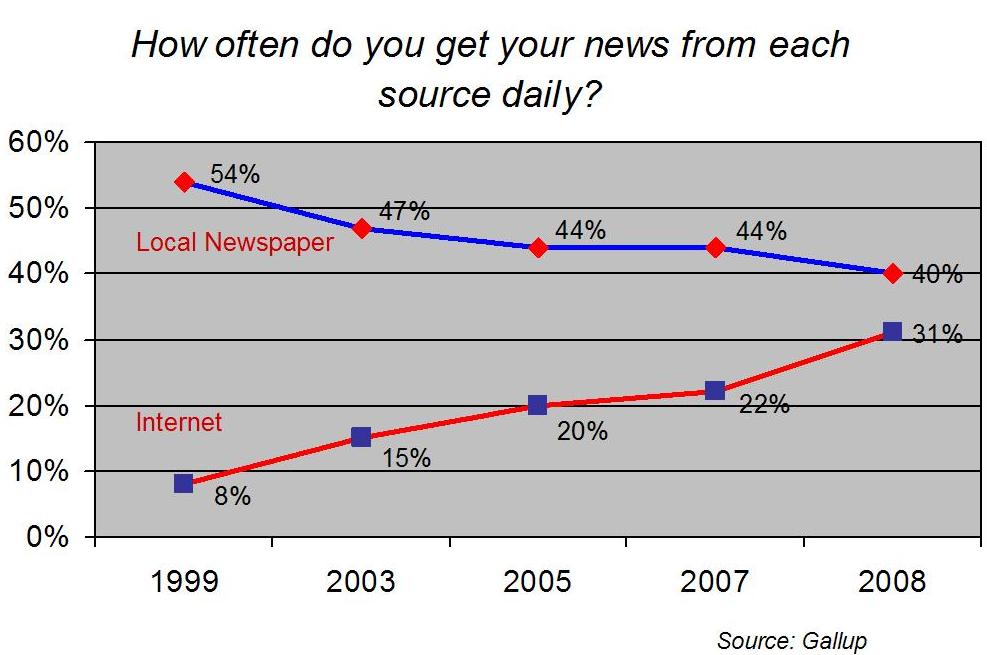
Gallup has issued its bi-annual report on news consumption trends, and all mainstream media are down with the exception of cable news and the Internet. The most striking finding is the percentage of people who say they consult the Internet for news every day: up 9% in two years to 31% today. The percentage has more than doubled in the last five years. Meanwhile, the percentage of people who consult a local newspaper every day has dropped from 54% in 1999 to 40% today.
For newspapers, the demographics are a horror show:
% of respondents who get their news every day from each source, by age group:
|
Age |
Local Newspapers |
Internet |
|
18-29 years |
22% |
36% |
|
30-49 |
34% |
42% |
|
50-64 |
42% |
27% |
|
65+ |
68% |
14% |
The statistics point to a continuing trend that has been hammering the newspaper industry: Young people don’t read newspapers. Meanwhile, Internet consumption is up across the board as people increasingly demand that news be delivered whenever they want it and wherever they happen to be.
Glimmer of Hope at the Rocky
E.W. Scripps says “a handful” of people have asked to look at the books of the Rocky Mountain News, a Denver institution that the company recently put up for sale. A spokesman said no one has yet offered to buy the troubled newspaper and that there’s no guarantee that the people who have asked to see the financials will be granted that access. However, the tire-kicking does indicate that not all hope is lost. Employees at the Rocky are trying to rally readers to their cause. A few of them have launched a site called I Want My Rocky to highlight the paper’s importance to the community and statements of support that have come in from readers. Thank God for WordPress.
Meanwhile, MediaNews CEO and Denver Post publisher Dean Singleton is wasting no time in taking advantage of his possible monopoly position. He’s told unions to reopen negotiations with an eye toward cutting $20 million in costs. The request came a day after Moody’s downgraded almost $1 billion of MediaNews debt out of fear of default. The Newspaper Guild represents 730 employees at The Post and the agency that administers the Post’s joint operating agreement with the Rocky.
Miscellany
The Atlanta Journal-Constitution is making its third round of job cuts in two years, eliminating 56 full-time and 100 part-time jobs in the circulation unit. The paper’s circulation has dropped 13.6 percent in the last year, according to the Audit Bureau of Control.
McClatchy’s November ad revenues were down 22% on an eye-popping 41% decline in classified advertising. E&P has the ugly breakdown: automotive advertising down 42.9%; real estate down 45.8%; and employment down 58.6%. We can’t remember any publisher reporting this kind of catastrophe over the last two years. Other trauma: retail ad revenue off 17.6%, national advertising down 33.2% and direct marketing off 16.8%. CEO Pat Talamantes said the declines were “in line with recent ad trends,” which has us wondering what other publishers are going to report.
The Tampa Tribune is blaming a rival newspaper for spreading rumors that it plans to exit the print business. In a co-bylined Sunday editorial, executive editor Janet Coats and publisher Denise Palmer said the rumors originated in the subscription sales department of competitor St. Petersburg Times. Coats and Palmer said the Times was taking advantage of its status as a privately owned company to position recent layoff reports at the Tribune as evidence that the paper would soon cease print operations. The rumor was also reported in the Tallahassee Democrat. Going on the offensive, Coats and Palmer claimed that the Tribune actually published more editorial pages than its rival in the first 10 days of December and that its willingness to report news of its own layoffs was in the best journalistic tradition that its rival has so far skirted. The publisher of the St. Petersburg Times countered, “Our circulation is growing nicely, and we’re very happy to have many readers in the Tampa Bay region.”
The New York Times‘s David Carr says newspapers have found an unlikely ally in besieged Illinois Governor Rod Blagojevich. According to a criminal complaint filed by the United States attorney, Blagojevich was obsessed with negative coverage by the Chicago Tribune, which has been campaigning for his impeachment. The governor allegedly threatened to withhold financial support for the Tribune unless the newspaper fired certain editorial writers. There is no evidence that the newspaper complied. Carr says the revelations about the Blagojevich’s criminal activities come at an odd time, given that the Tribune Company declared bankruptcy just one day before the scandal broke. “In a city and state where corruption is knit into the political fabric, a solvent daily paper would seem to be a civic necessity,” Carr writes. “But if another governor goes bad, what if the local paper were too diminished to do the job?”
The Financial Times profiles, New York Times Co. Chairman Arthur Sulzberger Jr., questioning whether he has the will and stamina to persevere through the industry downturn. “If the future of America’s newspaper business rests on one individual, it is on the 57-year-old former reporter,” the FT says. “Yet the fourth-generation family proprietor, who became publisher in 1992, is looking increasingly besieged.” You can say that again. The Times Company has over $1 billion in debt. It has been forced to consider asset sales and taking on even more debt to meet its obligations. The company was forced to cut its dividend by 74% last month, which the FT notes is “equivalent to [Sulzberger] asking his relatives to take an $18 million-a-year pay cut.” Meanwhile, Rupert Murdoch has made no bones about his intentions to take on the Times directly. All this is a heavy burden to bear, the story says, noting that Sulzberger’s legendary father, Arthur Ochs “Punch” Sulzberger, displayed backbone that has so far not been evident in his offspring.
More bad news for the Associated Press. The UK’s Guardian newspaper is reporting that Reuters and the Capitol Hill journalism boutique The Politico are teaming up. “The initiative will mean that more than 120 Washington-based journalists will be reporting full-time for Reuters and Politico by the time president-elect Barack Obama takes office in January,” says the Guardian, which has telegraphed its own intentions to enter in the US market. The Politico has been one of the few bright spots in American journalism this year, having signed up more than 100 newspapers for its Washington news service. Meanwhile, the AP has been under siege for its controversial fee structure and has recently lost some prominent subscribers.
 Esquire‘s 75th anniversary issue in October was a media sensation for its battery-powered cover and fat ad folio. But
Esquire‘s 75th anniversary issue in October was a media sensation for its battery-powered cover and fat ad folio. But